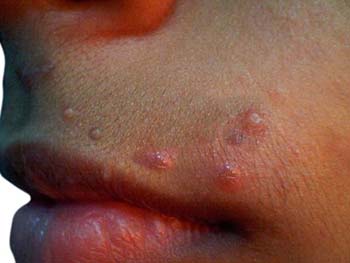
Molluscum contagiosum is a common viral skin infection that causes small, firm, raised spots on the skin. It is caused by a virus of the pox family and is most often spread through direct contact with an infected person or object. It can also be passed through sexual contact. The bumps usually appear on the face, neck, arms, and legs but can occur anywhere on the body.
They are usually painless and range in size from 2-5 mm in diameter. They may have a central indentation that looks like a dimple or pit. The infection is highly contagious and can spread quickly from person to person through direct contact or sharing of contaminated objects such as towels, clothing, and toys. Molluscum contagiosum is most common in children between the ages of 1-10 years old; however, it can affect adults as well.
While it is not serious and will usually go away without treatment within 6-12 months, it can be uncomfortable and unsightly for those affected.
Causes and Risk Factors of Molluscum Contagiosum
Molluscum contagiosum is a common skin condition caused by a virus. It is most often spread through direct contact with an infected person or object. It can also be spread through sexual contact or sharing items such as towels or clothing.
The virus that causes molluscum contagiosum is called the molluscipoxvirus. It can be spread through contact with an infected person’s skin, either directly or indirectly. It can also be spread through sexual contact, sharing items that have been contaminated with the virus, or by touching surfaces contaminated with the virus. People who are immunocompromised, such as those living with HIV/AIDS, are more likely to get molluscum contagiosum than those who have healthy immune systems.
Other risk factors include:
- -Living in warm and humid climates
- -Having close contact with someone who has molluscum contagiosum
- -Having a weakened immune system due to illness or medications
- – Mlb66 ir
- -Having skin conditions such as eczema or psoriasis
- -Using public pools, gyms, and other shared facilities where the virus may be present
- -Sharing personal items such as towels and clothing with someone who has molluscum contagiosum
- -Having unprotected sex with someone who has the condition
Molluscum contagiosum is highly contagious and can easily spread from person to person. It is important to take steps to prevent its spread, such as washing your hands frequently and avoiding direct contact with others who have it.
Symptoms of Molluscum Contagiosum
Molluscum contagiosum is a skin infection caused by a virus that is very common among children. It is highly contagious and can spread easily through skin-to-skin contact. The most common symptom of molluscum contagiosum is the appearance of small, firm, flesh-colored bumps on the skin. These bumps can range in size from a few millimeters to about one centimeter in diameter.
They may have a dimple or pit in the center and sometimes have a waxy or pearly appearance. In some cases, they may be itchy or sore. In addition to the bumps, other symptoms of molluscum contagiosum can include redness around the bumps, swollen lymph nodes in the area of infection, and mild fever. In some cases, infected individuals may also experience fatigue and general discomfort. However, these symptoms are usually mild and do not require medical treatment. It is important to note that molluscum contagiosum does not always cause visible symptoms.
In some cases, infected individuals may not experience any signs or symptoms at all and may only become aware of their infection when they notice that someone else has similar bumps on their skin. If you suspect that you or your child has molluscum contagiosum, it is best to consult with your doctor for diagnosis and treatment options.
Diagnosing Molluscum Contagiosum
Molluscum contagiosum is usually easy to diagnose, as the lesions it causes are distinct. A doctor will be able to identify them by sight alone. If the diagnosis is not clear, a doctor may take a sample of the fluid from inside a lesion for laboratory testing. This will confirm whether or not the virus is present. In some cases, a doctor may use a dermoscope to examine the lesions more closely. This is an instrument with a magnifying lens and bright light that allows doctors to get a closer look at the skin. If you suspect you have molluscum contagiosum, it’s best to see your doctor for an accurate diagnosis and treatment plan.